Best Antidepressant Discussions in Clinical Settings sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
Exploring the intricacies of antidepressants in clinical settings, this discussion delves into the nuances of treatment selection, efficacy considerations, and treatment guidelines, providing a comprehensive view of this essential aspect of mental health care.
Overview of Antidepressants
Antidepressants are medications commonly used in clinical settings to treat various mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety, and certain mood disorders. These medications work by affecting the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain, helping to improve mood and overall mental well-being.Classes of Antidepressants
Antidepressants are classified into several main classes based on their mechanism of action. The most commonly used classes of antidepressants include:- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): SSRIs are one of the most prescribed classes of antidepressants. They work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain. Examples of SSRIs include Prozac (fluoxetine), Zoloft (sertraline), and Lexapro (escitalopram).
- Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs): SNRIs work by increasing the levels of both serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain. Popular SNRIs include Cymbalta (duloxetine) and Effexor (venlafaxine).
- Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs): TCAs are an older class of antidepressants that are effective but often have more side effects compared to newer medications. Examples of TCAs include Elavil (amitriptyline) and Tofranil (imipramine).
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): MAOIs are another older class of antidepressants that are reserved for cases where other medications have not been effective. Examples of MAOIs include Nardil (phenelzine) and Parnate (tranylcypromine).
Each class of antidepressants has a unique mechanism of action that helps in alleviating symptoms of depression and other mental health conditions.
Factors Influencing Antidepressant Selection
When choosing an antidepressant for a patient, several factors need to be considered to ensure the most effective treatment plan. These include patient-specific factors, comorbidities, and side effect profiles.Patient-Specific Factors
Patient-specific factors play a crucial role in determining the choice of antidepressant. Factors such as age, gender, weight, metabolism, and previous history of response to antidepressants can all influence the selection process. For example, certain antidepressants may be more suitable for older adults due to their side effect profiles, while others may be preferred for younger patients.Comorbidities Impact
The presence of comorbidities can significantly impact the selection of antidepressants. Patients with comorbid conditions such as anxiety disorders, insomnia, or chronic pain may require antidepressants that can address these symptoms as well. It is essential to consider the interactions between different medications and how they may affect the overall treatment plan.Role of Side Effect Profiles
The side effect profiles of antidepressants play a crucial role in choosing the best option for a patient. Some patients may be more sensitive to certain side effects, such as weight gain, sexual dysfunction, or drowsiness. Understanding the potential side effects of each antidepressant and how they may impact the patient's quality of life is essential in making an informed decision.Efficacy and Effectiveness
Antidepressants are a crucial treatment option for various types of depression, but their efficacy can vary depending on the individual and the specific type of depression being addressed. It is essential to consider the effectiveness of antidepressants in clinical settings to ensure optimal outcomes for patients.Comparing Efficacy of Antidepressants
- SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors) like Prozac and Zoloft are commonly prescribed and have shown efficacy in treating mild to moderate depression.
- SNRIs (Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors) such as Cymbalta and Effexor are often used for major depressive disorder and have been found effective in some cases where SSRIs may not work.
- Atypical antidepressants like Wellbutrin and Remeron may be considered when other types of antidepressants have not been effective.
Individual Response to Antidepressants
Antidepressant response can vary greatly among individuals due to factors such as genetic makeup, coexisting medical conditions, and lifestyle factors. It is crucial for healthcare providers to monitor patients closely and adjust treatment plans based on individual responses to ensure the best outcomesMeasuring Antidepressant Effectiveness
- Monitoring symptoms: Regular assessment of depressive symptoms and improvement in mood can help gauge the effectiveness of an antidepressant.
- Side effects: Monitoring and managing side effects are essential to ensure that the benefits of the antidepressant outweigh any potential drawbacks.
- Functional improvement: Improvement in daily functioning, social interactions, and overall quality of life are key indicators of the effectiveness of an antidepressant.
Treatment Guidelines and Recommendations
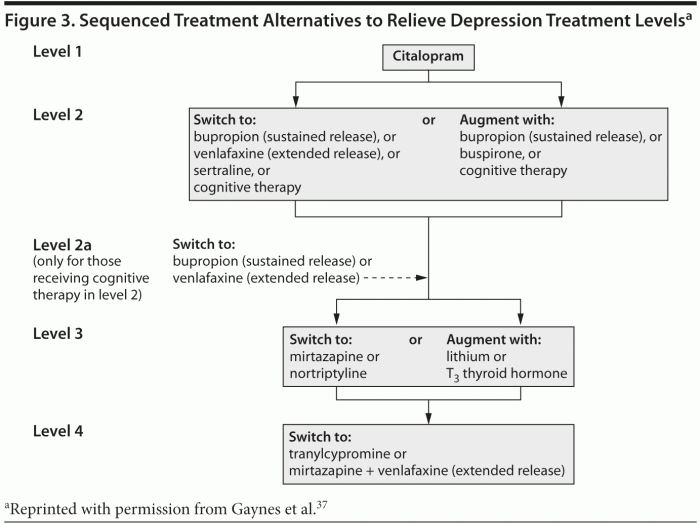 Antidepressants are commonly prescribed in clinical settings to manage various mental health conditions. It is important for healthcare providers to follow evidence-based treatment guidelines to ensure optimal outcomes for patients.
Antidepressants are commonly prescribed in clinical settings to manage various mental health conditions. It is important for healthcare providers to follow evidence-based treatment guidelines to ensure optimal outcomes for patients.Current Treatment Guidelines
- Antidepressant selection should be based on the patient's diagnosis, symptom severity, past treatment history, and potential side effects.
- Initial dosing and titration should follow recommended guidelines to achieve therapeutic levels while minimizing side effects.
- Regular monitoring of patients is essential to assess response to treatment, adjust dosages if needed, and monitor for potential adverse effects.
Importance of Evidence-Based Recommendations
Following evidence-based recommendations in clinical practice helps ensure that patients receive the most effective and safe treatment possible. It also allows healthcare providers to make informed decisions based on research and clinical experience.
Adapting Treatment Guidelines
While treatment guidelines provide a framework for prescribing antidepressants, there are scenarios where they may need to be adapted to meet the individual needs of patients. For example:
- In cases of treatment-resistant depression, combining different classes of antidepressants or adding adjunctive therapies may be necessary.
- Patients with certain medical conditions or co-occurring disorders may require adjustments to the standard treatment guidelines to avoid drug interactions or exacerbation of symptoms.
Last Word
In conclusion, the discussion on Best Antidepressant Discussions in Clinical Settings sheds light on the complexities of choosing the right antidepressant for patients, emphasizing the importance of individualized care and evidence-based practices in clinical settings. It serves as a valuable resource for healthcare professionals navigating the landscape of antidepressant therapy.
FAQ Resource
What factors influence the selection of antidepressants?
Factors such as patient-specific characteristics, comorbidities, and side effect profiles play a crucial role in determining the choice of antidepressant.
How can the efficacy of antidepressants be measured in a clinical setting?
Efficacy can be evaluated by assessing the response of patients to different antidepressants and monitoring their symptoms over time.
Are there scenarios where treatment guidelines for antidepressants may need to be adapted?
Yes, treatment guidelines may need to be adjusted based on individual patient needs, especially in cases where standard recommendations may not be suitable.